Abstract:
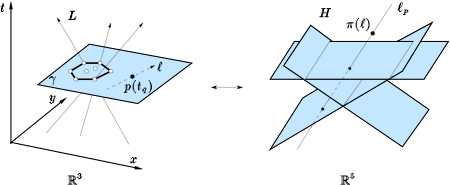
The ability to represent and query continuously moving objects is important in many applications of spatio-temporal database systems. In this paper we develop data structures for answering queries on moving objects and study tradeoffs between various performance measures--query time, size, and accuracy of the result.
 Publications -
Jeff Erickson
(jeffe@cs.uiuc.edu)
09 Apr 2004
Publications -
Jeff Erickson
(jeffe@cs.uiuc.edu)
09 Apr 2004